DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID
WHAT IS SELECTIVE CATALYTIC REDUCTION (SCR) ?
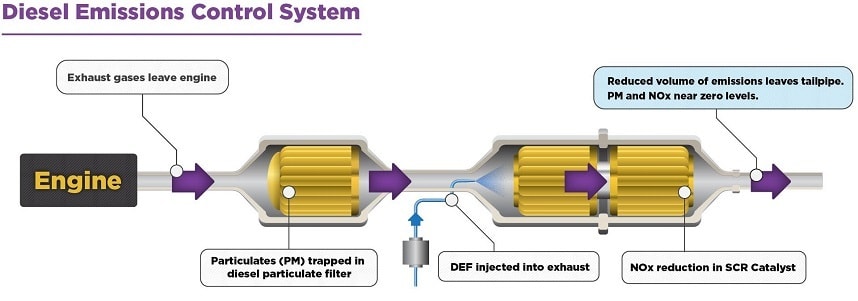
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is an advanced active emissions control technology system that injects a liquid-reductant agent through a special catalyst into the exhaust stream of a diesel engine. The reductant source is usually automotive-grade urea, otherwise known as Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF). The DEF sets off a chemical reaction that converts nitrogen oxides into nitrogen, water and tiny amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), natural components of the air we breathe, which is then expelled through the vehicle tailpipe.
SCR technology is designed to permit nitrogen oxide (NOx) reduction reactions to take place in an oxidizing atmosphere. It is called "selective" because it reduces levels of NOx using ammonia as a reductant within a catalyst system. The chemical reaction is known as "reduction" where the DEF is the reducing agent that reacts with NOx to convert the pollutants into nitrogen, water and tiny amounts of CO2. The DEF can be rapidly broken down to produce the oxidizing ammonia in the exhaust stream.SCR technology alone can achieve NOx reductions up to 90 percent.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS TO UTILIZING SCR TECHNOLOGY?

SCR technology does not change the design or operation of the engine but does allow manufacturers to tune engines to boost performance, increase engine reliability and achieve fuel savings.
Engines equipped with SCR are able to function at optimal combustion temperatures, which increases fuel efficiency and contributes to the production of engine power. One of the greatest benefits fleet managers recognize with SCR technology is the cost savings associated with increased fuel efficiency. Post 2016 heavy-duty trucks by Tata Motors, Ashok Leyland, Bharat Benz and Mahindra can achieve fuel savings of around 5% compared to pre 2016 models with similar engine specifications; off-road machines with SCR also report fuel savings of 5% and higher.
SCR also results in longer overall engine life, as there is a reduced dependency on exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), less heat rejection and greater component reliability.
WHAT IS ADBLUE® ?
AdBlue® (Diesel Exhaust Fluid) is a 32.5% solution of urea in deionised water and is required by many commercial vehicles operating on Europe's roads. AdBlue® (Diesel Exhaust Fluid)is essential for the correct operation of an advanced pollution control technology installed in the exhaust system called Selective Catalytic Reduction or SCR. Unlike diesel, AdBlue® is a clear, non-toxic liquid that is safe to handle and does not damage the environment. AdBlue® is not a fuel or fuel additive.
WHO NEEDS ADBLUE® ?
Currently, AdBlue® is required by the majority of heavy duty diesel vehicles (trucks, buses and coaches) purchased after October 2006.
In order to meet the Euro IV and V emissions limits, all of the major European truck makers, to greater or lesser extent, offer SCR equipped vehicles. However, MAN and Scania have a firm focus on an alternative technology called EGR that does not require the use of AdBlue® and have equipped the majority of their model ranges accordingly.
It is important to ensure that the vehicles remain supplied with AdBlue®, as an on-board policing system will enforce a torque penalty if the AdBlue® tank is empty. This is to ensure that the vehicles NOx emissions remain below the legal limit.
FEATURES
Non Toxic & Non Hazardous.
Non Flammable.
Compatible with all diesel SCR systems.
Reduces SCR component wear.
Do not mix with water.
Meets OEM specifications.
Extends SCR catalyst life.
WHAT ARE EURO IV AND V?
The European Commission sets the limits for harmful pollutants - including NOx and particulate matter (PM) - within its Euro IV and V legislation. The legislation is binding and limits the emissions of all vehicles >3.5t registered after the implementation date. Euro IV was implemented in 2006 and Euro V in October 2009. All new registrations within the European Union must meet Euro V emissions standards.
VIDEO
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
| Characteristics | Unit | Limits | Test methods | |
| Min | Max | |||
| Urea content a | % (m/m)d | 31.8 | 33.2 | ISO 22241-2 Annex B e ISO 22241-2Annex Ce |
| Density at 20 aC b | kg/m3 | 1 087.0 | 1 093.0 | ISO 3675 or ISO 12185 |
| Refractive index at 20 aC c | - | 1,381 4 | 1,384 3 | ISO 22241-2 Annex C |
| Alkalinity as NH3 | % (m/m)d | - | 0.2 | ISO 22241-2 Annex D |
| Biurret | % (m/m)d | - | 0.3 | ISO 22241-2 Annex E |
| Aldehydes | mg/kg | - | 5 | ISO 22241-2 Annex F |
| Insoluble matter | mg/kg | - | 20 | ISO 22241-2 Annex G |
| Phosphate (PO4) | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | ISO 22241-2 Annex H |
| Calcium | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | ISO 22241-2 Annex I |
| Iron | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | |
| Copper | mg/kg | - | 0.2 | |
| Zinc | mg/kg | - | 0.2 | |
| Chromium | mg/kg | - | 0.2 | |
| Nickel | mg/kg | - | 0.2 | |
| Aluminium | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | |
| Mangnesium | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | |
| Sodium | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | |
| Potassium | mg/kg | - | 0.5 | |
| Identity | - | Identical to reference | ISO 22241-2 Annex J | |
STORAGE AND HANDLING
It is essential that the purity of AdBlue® is ensured throughout the supply chain and when stored at a home depot. Therefore, it is critical that AdBlue® is transported and stored in a manner that conforms to the CEFIC guidelines. When stored at a home depot, it is important that the AdBlue® is not decanted from IBCs or bulk containers into smaller canisters as SCR catalysts are sensitive to many contaminants - especially mineral ions - and can suffer irreversible damage. If the damage has resulted from mishandling of AdBlue®, the vehicle's warranty is likely to be found invalid.
To some extent AdBlue® is sensitive to extreme temperatures, both hot and cold. The solution will freeze if its temperature falls below -11°C, and the urea content can decrease if stored at temperatures in excess of 30°C. However, AdBlue® is not harmed by the freezing process and once thawed will retain its concentration and quality. In areas where the temperature is frequently in excess of 30°C (Greece, Spain etc.) it is necessary to ensure that the solution is not stored in direct sunlight.
The trucks themselves, and larger equipment installations, are built with several heated components to minimise the problem of frozen AdBlue®.
PACKAGING SIZE AVAILABLE
20 Liter
25 Liter
210 Liter
FAQ
If Inabgo is 32.5 % Urea solution can I make it at home with the urea obtained in my farms ?
NO! Fertiliser grade urea is impure urea which contains high percentage of biuret, aldehydes and other inorganic substances that deactivate the catalyst in the SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system. These impurities cause a permanent damage to the system and would lead to a high capital maintenance in few months.
Another problem with using fertiliser grade urea is, government since it is subsidised is masked with neem oil or other additives so people do not use it for industrial use. Since neem oil and other additives deactivate catalyst it I not at all recommended to use fertiliser grade urea.
Lastly it is illegal to use subsidised urea for manufacturing other product than meant for agricultural use.
Can I use tap water or mineral water in Adblue® tank ?
NO! Tap water or even mineral or drinking water contains many salts and minerals which block catalysts sight that are used by SCR SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system. This damages the catalyst and you may have to incur change of catalyst system which is a very costly affair
Can I use Adblue in Euro III or BS III engines as I care about environment ?
NO! Only BS- IV vehicles which have SCR systems installed can you Inabgo.
Is Adblue® added in Diesel tank as additive ?
No! There is a separate tank for adblue. Adblue is not added to the engine but is only used to reduce the improperly burned and harmful nitrous oxide gases. Never add Adblue in diesel tank.
Can Using Adblue Improve Diesel Mileage or Diesel Average ?
Yes! the fuel consumption is lower by 3% to 4 % in the case of engines compliant with BS IV or EURO 4 norms and the saving could be about 5% for vehicles complying to Euro 5 norms.
Why is Inabgo Adblue® quantity needed less than other Adblue suppliers ?
We at Inabgo make sure that right concentration of Urea is maintained, while other manufacturers try to reduce their cost by providing 31.8% urea solution which still passes ISO 222 41 we at Inabgo Maintain 33.2 % which though passes again ISO 222 41 but our customers get more for less a core value here at Inabgo.
Can I use metal funnels or buckets ?
Adblue is complaint to SS 316, 304 and other high grade metal alloys that are not available in local market. Adblue is not compatible with Mild steel or galvanised steel or aluminium. So use only polypropylene or polyethylene or HDPE equipments for your benefit we sale Adblue friendly transfer materials.
Can I use diesel cans/ Drums which were used for oil or diesel to transport Adblue® ?
No! Oil or diesel damages spraying of adblue to the system and only a drop of diesel can pollute 20 L of adblue solution. So proper care should be taken to transfer adblue from barrels or drums to the Adblue tank.
Is Every Urea Solution Adblue® ?
No! Purity of Adblue is most critical, it is not the cost of urea, it is cost of removing the impurities which save the expensive catalyst.
What is this Catalyst that you say is so expensive and how expensive is this catalyst ?
The SCR System contain a mixture of Palladium (18,00,000/ kg) , Rhodium and platinum (25,00,000/kg) which is similar or more costlier than gold. Now compare this to 50/Kg approx. price of Inabgo. So what will you risk?
*note price of metals are day specific and are considered for example purposes.











